Introduction
The way we engage with the world around us has been completely transformed by the Internet of Things (IoT). From smart homes and wearable devices to industrial automation and smart cities, IoT is transforming every aspect of our lives. However, as the number of connected devices grows, so does the potential for security breaches. Ensuring robust IoT security is critical to protect data, privacy, and the integrity of the entire connected ecosystem.
Definition
IoT security is the all-encompassing set of procedures, guidelines, and technological advancements intended to shield networks and Internet of Things (IoT) devices against intrusions, assaults, and breaches. It encompasses securing the hardware, software, communication channels, and data associated with IoT devices, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the information they process and transmit. Effective IoT security involves robust authentication and authorization mechanisms, data encryption, secure firmware updates, and continuous monitoring and threat detection to safeguard against vulnerabilities and evolving cyber threats in a highly interconnected ecosystem.
The Proliferation of IoT Devices
The IoT ecosystem comprises a vast array of devices, including sensors, actuators, smart appliances, and industrial equipment. These devices communicate with each other and with central servers or cloud platforms, often without human intervention. According to estimates, the number of IoT devices worldwide is expected to surpass 75 billion by 2025. This explosive growth underscores the need for comprehensive security measures to prevent unauthorized access and malicious activities.
Key Security Challenges in IoT
1. Device Heterogeneity
The variety of platforms and devices is one of the main obstacles to IoT security. The hardware capabilities, operating systems, and communication protocols of Internet of Things devices differ greatly from one another. It is challenging to apply a security solution that is appropriate for every situation due to this variability. Customised security protocols are needed for every device, taking into consideration its unique strengths and weaknesses.
2. Limited Computing Resources
Many IoT devices are designed to be small, low-cost, and energy-efficient. As a result, they often have limited computing power, memory, and storage. These constraints can hinder the implementation of advanced security features such as encryption, intrusion detection, and secure firmware updates. Balancing security with performance and cost is a critical challenge for IoT device manufacturers.
3. Scalability
The sheer scale of IoT deployments poses significant security challenges. Managing security for millions or even billions of devices requires robust and scalable solutions for device authentication, data encryption, and access control. Centralized security management systems must be capable of handling the vast number of devices and their associated data streams.
4. Interoperability
IoT ecosystems often consist of devices from multiple manufacturers, each with its own proprietary protocols and standards. Ensuring interoperability while maintaining security is a complex task. Standardization efforts, such as those led by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC), aim to address these challenges by developing common security frameworks and protocols.
5. Physical Security
Unlike traditional IT devices, many IoT devices are deployed in physically accessible locations, making them vulnerable to tampering and physical attacks. Ensuring physical security is essential to prevent unauthorized access to the device hardware and firmware. Measures such as tamper-evident packaging, secure boot mechanisms, and hardware security modules can help mitigate these risks.
Core Principles of IoT Security
To address the aforementioned challenges, a comprehensive IoT security strategy should be based on several core principles:
1. End-to-End Security
IoT security should encompass the entire lifecycle of the device, from manufacturing and deployment to operation and decommissioning. This includes securing the device hardware, firmware, software, communication channels, and data storage. End-to-end security ensures that every component of the IoT ecosystem is protected against potential threats.
2. Strong Authentication and Authorization
Robust authentication mechanisms are essential to verify the identity of devices and users. This can include the use of digital certificates, cryptographic keys, and secure tokens. In addition, granular authorization policies should be implemented to control access to sensitive data and functions based on the principle of least privilege.
3. Data Encryption
Encryption is a fundamental component of IoT security, protecting data both at rest and in transit. Strong encryption algorithms should be used to secure communication channels between devices and servers, as well as to protect stored data from unauthorized access. Additionally essential are routine key management procedures including safe key storage and key rotation.
4. Secure Firmware Updates
IoT devices must be able to receive and install firmware updates securely to address vulnerabilities and add new features. Secure firmware update mechanisms should include integrity checks, authentication of the update source, and protection against rollback attacks. Over-the-air (OTA) updates are commonly used to distribute firmware updates to a large number of devices efficiently.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
To quickly discover and address security incidents, proactive monitoring and threat detection are crucial. This can involve the use of intrusion detection systems (IDS), anomaly detection algorithms, and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions. Continuous monitoring helps to detect potential threats early and initiate appropriate response actions.
Emerging Trends in IoT Security
The dynamic nature of the IoT landscape means that security strategies must continuously evolve to address new threats and challenges. Several emerging trends are shaping the future of IoT security:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being increasingly integrated into IoT security solutions. AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of security threats. These technologies enable more accurate threat detection, faster response times, and adaptive security measures that evolve with the threat landscape.
2. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger that can enhance IoT security. Blockchain can be used to securely record device identities, transactions, and data exchanges, providing an immutable audit trail. This can help prevent unauthorized access, data tampering, and ensure the integrity of the IoT ecosystem.
3. Edge Computing
By processing data closer to the source, edge computing lowers latency and bandwidth consumption. In the context of IoT security, edge computing can enhance security by enabling real-time threat detection and response at the edge of the network. This reduces the reliance on centralized security systems and improves the overall resilience of the IoT infrastructure.
4. Zero Trust Architecture
The zero trust security model operates on the principle that no device or user should be trusted by default, regardless of their location. In an IoT environment, zero trust architecture involves continuously verifying the identity and integrity of devices and users, enforcing strict access controls, and monitoring all network traffic for suspicious activities. This approach helps to mitigate the risk of insider threats and lateral movement within the network.
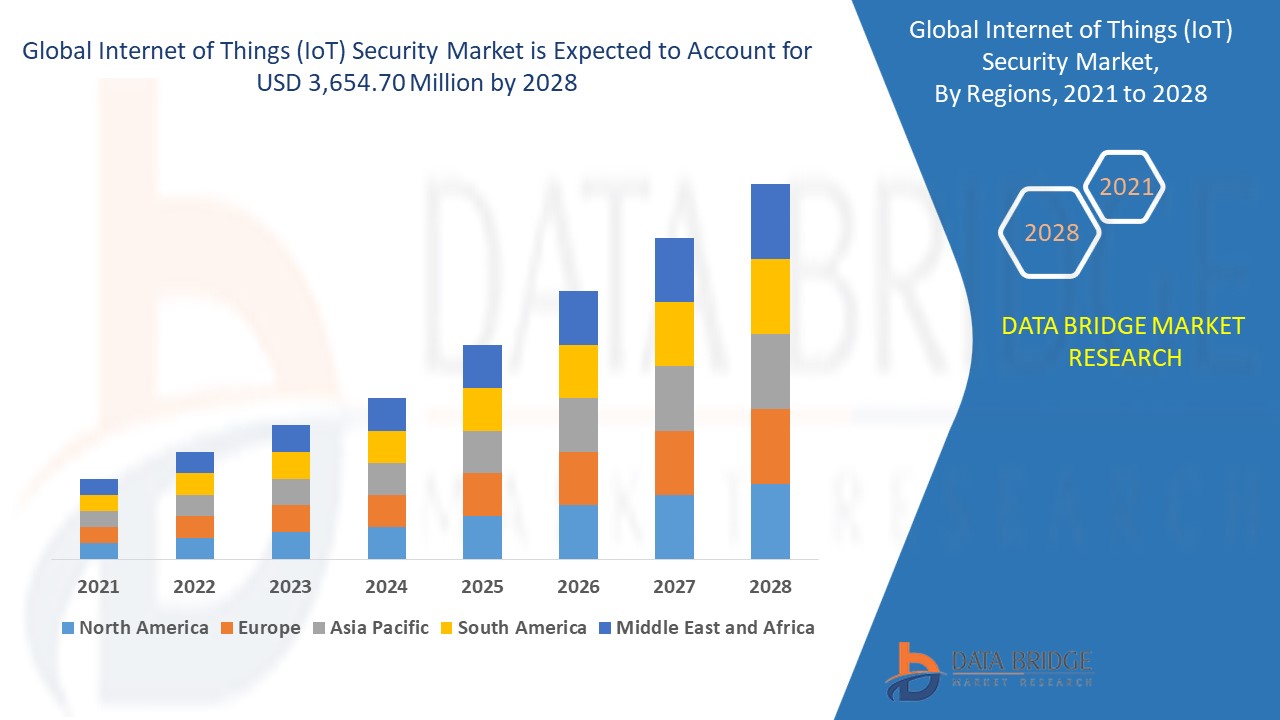
Growth Rate of Internet of Things (IoT) Security Market
It is expected that the market for internet of things (IoT) security would expand at a rate of 11.20% between 2021 and 2028, with a projected value of USD 3,654.70 million at that time.
Learn more: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-internet-of-things-iot-security-market
Conclusion
As the IoT ecosystem continues to expand, the importance of robust security measures cannot be overstated. The diverse and dynamic nature of IoT devices, coupled with their critical roles in various sectors, makes them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Ensuring IoT security requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses device heterogeneity, limited computing resources, scalability, interoperability, and physical security. In an increasingly interconnected world, the security of IoT devices is paramount to safeguarding data, privacy, and the integrity of critical infrastructure. As we embrace the benefits of IoT, we must remain vigilant and proactive in addressing security challenges to ensure a safe and secure digital future.