Experiencing chest tightness and shortness of breath can be distressing and may indicate various underlying medical conditions. These symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe respiratory distress, impacting daily activities and quality of life. This blog explores common causes of chest tightness and shortness of breath, effective strategies for relief, when to seek medical help, and preventive measures to maintain respiratory health. Aerocort Inhaler Uses is a combination of Levosalbutamol and Beclomethasone.
Understanding Chest Tightness and Shortness of Breath:
Chest tightness is often described as a sensation of pressure or squeezing in the chest, sometimes accompanied by discomfort or pain. Shortness of breath, also known as dyspnea, refers to difficulty breathing or a feeling of not getting enough air. These symptoms can occur suddenly or develop gradually, depending on their underlying cause: Buy Aerocort Inhaler is used to relieve symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, breathing difficulty, coughing, etc.
-
Causes of Chest Tightness and Shortness of Breath:
-
Respiratory Conditions: Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and bronchitis.
-
Cardiovascular Issues: Heart attack, angina (chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart), heart failure, and arrhythmias.
-
Anxiety and Stress: Panic attacks and anxiety disorders can cause hyperventilation and chest discomfort.
-
Allergies: Allergic reactions to pollen, dust, pet dander, or food can lead to respiratory symptoms.
-
Physical Activity: Intense exercise or exertion can cause temporary shortness of breath.
-
-
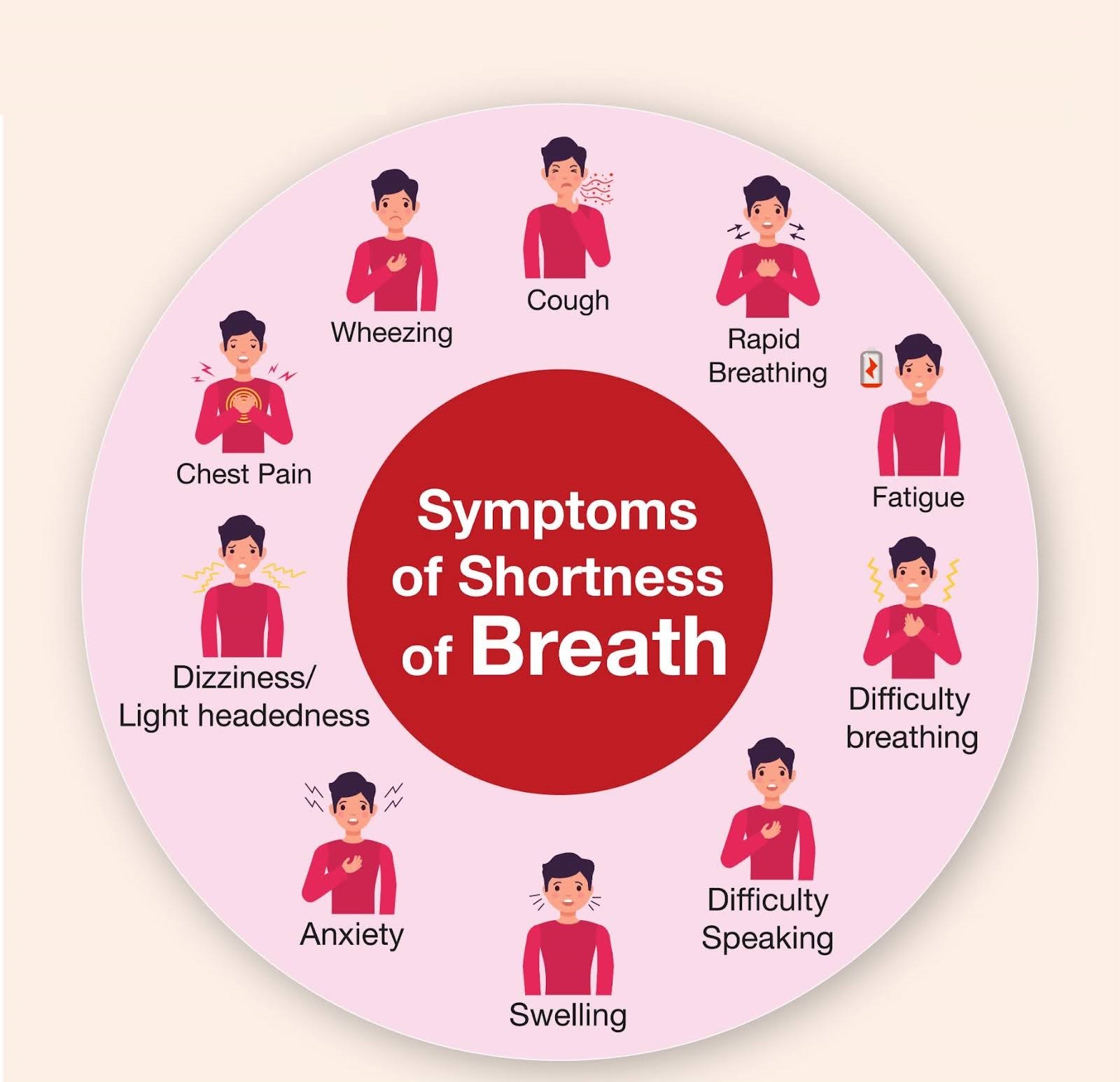
Symptoms Associated with Chest Tightness and Shortness of Breath:
- Rapid or shallow breathing
- Wheezing or coughing
- Pain or discomfort in the chest
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy
- Sweating
- Bluish lips or nails (in severe cases)
Effective Strategies for Relief:
When experiencing chest tightness and shortness of breath, several strategies can provide relief and improve respiratory comfort:
-
Immediate Actions:
-
Stay Calm: Anxiety can exacerbate symptoms. Focus on slow, deep breathing exercises to promote relaxation.
-
Change Positions: Sitting upright or leaning forward can ease breathing by expanding lung capacity.
-
Loosen Clothing: Tight clothing around the chest can restrict breathing. Wear loose-fitting garments.
-
Use of Rescue Inhalers: For individuals with asthma or COPD, using prescribed rescue inhalers (e.g., albuterol) as directed can quickly relieve symptoms.
-
Seek Fresh Air: Move to a well-ventilated area or open a window to improve air circulation.
-
-
Longer-Term Management Strategies:
-
Medication Adherence: Take prescribed medications regularly to manage underlying conditions such as asthma, COPD, or heart disease.
-
Pursed Lip Breathing: Inhale slowly through your nose and exhale through pursed lips to improve airflow and reduce shortness of breath.
-
Relaxation Techniques: Practice meditation, yoga, or guided imagery to reduce stress and anxiety, which can help control breathing patterns.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep respiratory mucous membranes moist and facilitate easier breathing.
-
Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid triggers such as allergens, smoke, pollutants, or strenuous activities that worsen symptoms.
-
-
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments:
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can strain the respiratory system. Aim for a balanced diet and regular exercise to support lung function.
-
Humidify the Air: Use a humidifier, especially during dry seasons or in heated indoor environments, to prevent respiratory irritation.
-
Elevate Head During Sleep: Prop yourself up with pillows to reduce pressure on the chest and improve breathing while sleeping.
-
-
Medical Evaluation and Treatment:
-
Consult Healthcare Provider: Seek medical evaluation if chest tightness and shortness of breath persist, worsen, or are accompanied by chest pain, fainting, or bluish discoloration.
-
Diagnostic Tests: Your healthcare provider may perform tests such as spirometry (lung function tests), chest X-ray, electrocardiogram (ECG), or blood tests to diagnose underlying conditions.
-
Treatment Options: Depending on the diagnosis, treatments may include bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antibiotics (if infection is present), or cardiac medications to manage heart-related symptoms.
-
When to Seek Medical Help:
Prompt medical attention is essential if you experience the following symptoms along with chest tightness and shortness of breath:
- Severe chest pain or pressure
- Difficulty speaking due to shortness of breath
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Fainting or loss of consciousness
- Bluish discoloration of the lips or nails
These signs may indicate a medical emergency such as a heart attack, severe asthma attack, or pulmonary embolism, requiring immediate evaluation and treatment.
Preventive Measures for Respiratory Health:
To maintain respiratory health and reduce the risk of chest tightness and shortness of breath:
-
Quit Smoking: Smoking damages the lungs and exacerbates respiratory conditions. Seek support to quit smoking if you currently smoke.
-
Stay Active: Regular exercise improves lung function and overall cardiovascular health.
-
Monitor Allergies: Identify and avoid triggers that worsen respiratory symptoms, and consider allergy testing if needed.
-
Annual Flu Vaccine: Reduce the risk of respiratory infections by getting vaccinated against influenza annually.
-
Manage Chronic Conditions: Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing chronic conditions such as asthma, COPD, or heart disease.
Conclusion:
Chest tightness and shortness of breath can stem from various causes, ranging from respiratory and cardiovascular conditions to anxiety and physical exertion. Effective management involves understanding the underlying cause, employing immediate relief strategies, and seeking medical evaluation if symptoms persist or worsen. By practicing preventive measures, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and adhering to medical treatments, individuals can enhance respiratory health, alleviate symptoms, and improve overall quality of life. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance and treatment recommendations based on your specific symptoms and medical history. Prompt attention to respiratory symptoms ensures timely intervention and optimal management of chest tightness and shortness of breath, promoting respiratory well-being and enhanced quality of life.